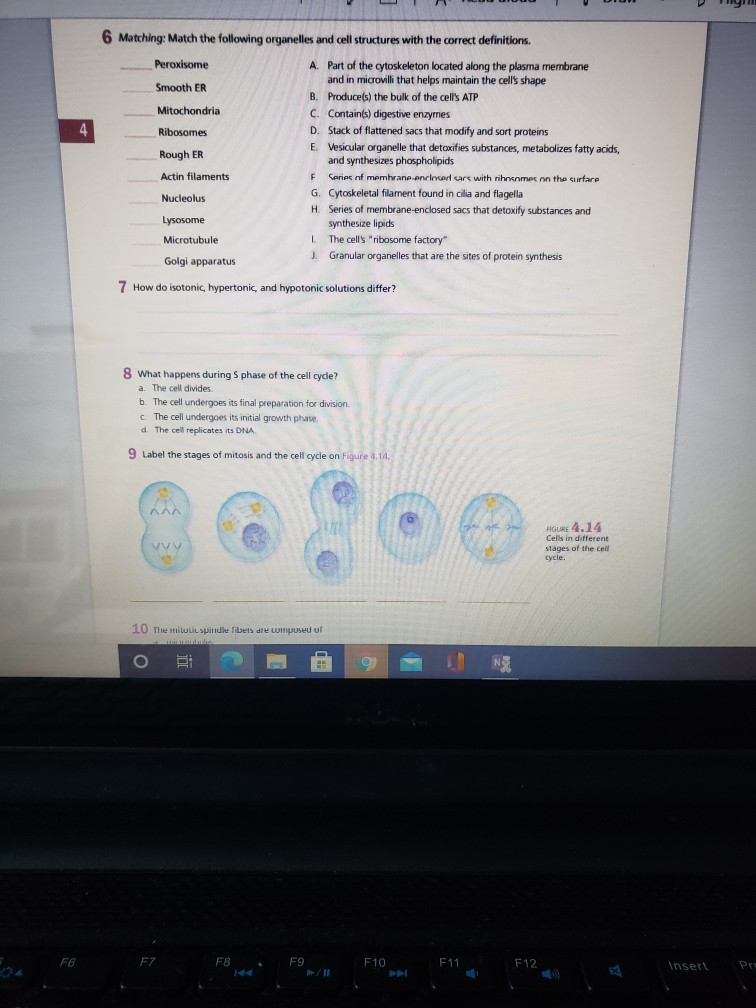
44 identify the structures in the cell pictured on the right. label a label b label c label d label e
Parts of a microscope with functions and labeled diagram - Microbe Notes Q. List down the 18 parts of a Microscope. 1. Ocular Lens (Eye Piece) 2. Diopter Adjustment 3. Head 4. Nose Piece 5. Objective Lens 6. Arm (Carrying Handle) 7. Mechanical Stage 8. Stage Clip 9. Aperture 10. Diaphragm 11. Condenser 12. Coarse Adjustment 13. Fine Adjustment 14. Illuminator (Light Source) 15. Stage Controls 16. Base 17. 4.2: IR Spectroscopy - Chemistry LibreTexts For every function group within a molecule, such as the C≡N triple bond in phenyl selenocyanate (C 6 H 5 SeCN) or the C-D single bond in deuterated chloroform (DCCl 3), they have an individual infrared vibrational mode and associated energy levels. For a typical 3-level system (Figure \(\PageIndex{24}\), both the 0 to 1 and the 1 to 2 ...
Human body systems: Overview, anatomy, functions | Kenhub The skeletal system is composed of bonesand cartilages. There are two parts of the skeleton; axial and appendicular. The axial skeleton consists of the bones of the headand trunk. The appendicular skeleton consists of the bones within the limbs, as well as supporting pectoral and pelvic girdles. There are 206 bones in an adult human body.
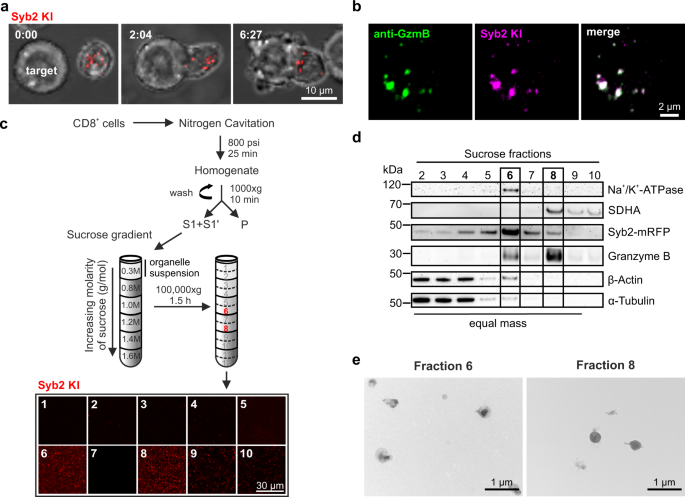
Identify the structures in the cell pictured on the right. label a label b label c label d label e
: Free Bibliography & Citation Maker - MLA, APA, Chicago ... BibMe Free Bibliography & Citation Maker - MLA, APA, Chicago, Harvard en.wikipedia.org › wiki › ArchaeaArchaea - Wikipedia The classification of archaea, and of prokaryotes in general, is a rapidly moving and contentious field. Current classification systems aim to organize archaea into groups of organisms that share structural features and common ancestors. 3.1: Types of Chemical Compounds and their Formulas A Identify the symbol for each element in the molecule. Then identify the substance as either an organic compound or an inorganic compound. ... B As with all organic compounds, C and H are written first in the molecular formula. ... \label{3.1.1}\] where \(Q_1\) and \(Q_2\) are the electrical charges on particles 1 and 2, and \(r\) is the ...
Identify the structures in the cell pictured on the right. label a label b label c label d label e. Nucleotide - Genome.gov A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). In RNA, the base uracil (U) takes the ... Endospore Staining: Principle, Procedure, Results - Microbe Online Make a smear on a clean glass slide. Allow the slide to dry (air dry) and then heat fix Place a blotting paper on the slide (covering the smear) and saturate with carbolfuchsin to steam (for about 5 minutes). This should be repeated while adding drops of carbolfuchsin and avoiding overheating (simply heat to steam) Different Size, Shape and Arrangement of Bacterial Cells Spirilla (or spirillum for a single cell) are curved bacteria which can range from a gently curved shape to a corkscrew-like spiral. Many spirilla are rigid and capable of movement. A special group of spirilla known as spirochetes are long, slender, and flexible. 1. Vibrio Identify the structures in the cell pictured on the right. Label A ... Identify the structures in the cell pictured on the right. Label A Label B Label C Label D Label E Get the answers you need, now! haleighhight0 haleighhight0 05/26/2022 Biology College answered Identify the structures in the cell pictured on the right. Label A Label B
Cell Organelles- Definition, Structure, Functions, Diagram In a plant cell, the cell wall is made up of cellulose, hemicellulose, and proteins while in a fungal cell, it is composed of chitin. A cell wall is multilayered with a middle lamina, a primary cell wall, and a secondary cell wall. The middle lamina contains polysaccharides that provide adhesion and allow binding of the cells to one another. › 43492956 › INTERCHANGE_5ta_EDICION(PDF) INTERCHANGE 5ta EDICION - Academia.edu Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. › science › articleMetabolic cycles and signals for insulin secretion ... Jul 05, 2022 · (C and D) Putative assignments of metabolic cycles (blue boxes), as well as NADH and NADPH shuttles and shunts (orange and green boxes, respectively), are shown for Mito Cat (C) and Mito Ox (D). GAPDH during glycolysis reduces NAD + in the cytosol that has to be reoxidized during Mito Cat to maintain glycolytic flux. This occurs through the ... Karyotype - Genome.gov A karyotype is an individual's complete set of chromosomes. The term also refers to a laboratory-produced image of a person's chromosomes isolated from an individual cell and arranged in numerical order. A karyotype may be used to look for abnormalities in chromosome number or structure. Narration 00:00 …
Label Worksheet Cell Prokaryotic Prokaryotic cells 2. Whereas eukaryotic cells have many different functional compartments, divided by membranes, prokaryotes only have one membrane (the plasma membrane) enclosing all of the cell's internal contents BY 124 SI Worksheet 1: Chapters 29-30 Showing top 8 worksheets in the category - Label Animal Cells b) What would happen if an ... Types of tissue: Structure and function | Kenhub The cells of epithelial tissue have three types of surfaces differentiated by their location and functional specializations: basal, apical, and lateral. Basal surface The basal surface is nearest to the basement membrane. The basement membraneitself creates a thin barrier between connective tissues and the most basal layer of epithelial cells. Base Pair - Genome.gov A base pair consists of two complementary DNA nucleotide bases that pair together to form a "rung of the DNA ladder." DNA is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder — a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. Organelle - Genome.gov Definition. An organelle is a subcellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell, much like an organ does in the body. Among the more important cell organelles are the nuclei, which store genetic information; mitochondria, which produce chemical energy; and ribosomes, which assemble proteins.
Identify the structures in the cell pictured on the right. Label A E ... Identify the structures in the cell pictured on the right. Label A E Label B Label C D Label D Label E DONE No
CHE 120 - Introduction to Organic Chemistry - Textbook The amino acids found in proteins are L-amino acids. Exercises 1. Write the side chain of each amino acid. a. serine b. arginine c. phenylalanine 2. Write the side chain of each amino acid. a. aspartic acid b. methionine c. valine 3. Draw the structure for each amino acid. a. alanine b. cysteine c. histidine 4.
EOF
Identify the structures in the cell pictured on the right. Label A ... answered Identify the structures in the cell pictured on the right. Label A Label B Label C Label D A prokaryotic cell is labeled. Part A is the outside of the cell. Part B is the inside of the cell. Part C are the small dots inside the cell. Part D is the large swirly structure inside of the cell. Answer 2 people found it helpful ray77777777777777
Polypeptide Structure & Examples | What is a Polypeptide? - Video ... 15. chemical reaction that joins two amino acids together and releases a water molecule. 16. is a chain of more than 50 amino acids. Down. 1. may consist of more than one polypeptide. 2. a ...
Bones of the orbit: Anatomy, foramina, walls and diagram - Kenhub The orbit appears as a quadrangular pyramidal cavern in the upper face. It is made up of four facial bones and three cranial bones: maxilla, zygomatic bone, lacrimal bone, palatine bone, frontal bone, ethmoid bone, and sphenoid bone . The base of this pyramid opens anteriorly onto the face, while the apex is pointed posteromedially towards the ...
› doc › 123745376Biochemistry PDF | PDF | Cell (Biology) | Biochemistry - Scribd Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton acts to organize and maintain the cell's shape; anchors organelles in place; helps during endocytosis, the uptake of external materials by a cell, and cytokinesis, the separation of daughter cells after cell division; and moves parts of the cell in processes of growth and mobility. The eukaryotic cytoskeleton is ...
quizlet.com › 520218106 › science-s1-flash-cardsScience S1 Flashcards | Quizlet Analogous structures do not indicate a common ancestor. Analogous structures have the same structure, but may have a different function. Analogous structures have the same function but a different structure. An example of an analogous structure is the wing of a bat and a butterfly.
› solution-answer › chapter-17Chapter 17, Problem 44P | bartleby Textbook solution for University Physics Volume 1 18th Edition William Moebs Chapter 17 Problem 44P. We have step-by-step solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts!
3.1: Types of Chemical Compounds and their Formulas A Identify the symbol for each element in the molecule. Then identify the substance as either an organic compound or an inorganic compound. ... B As with all organic compounds, C and H are written first in the molecular formula. ... \label{3.1.1}\] where \(Q_1\) and \(Q_2\) are the electrical charges on particles 1 and 2, and \(r\) is the ...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › ArchaeaArchaea - Wikipedia The classification of archaea, and of prokaryotes in general, is a rapidly moving and contentious field. Current classification systems aim to organize archaea into groups of organisms that share structural features and common ancestors.
: Free Bibliography & Citation Maker - MLA, APA, Chicago ... BibMe Free Bibliography & Citation Maker - MLA, APA, Chicago, Harvard

![Expert Answer] please help 30 points identify the structures ...](https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/d85/7478e9834853653c35f997b51ad2e63b.png)
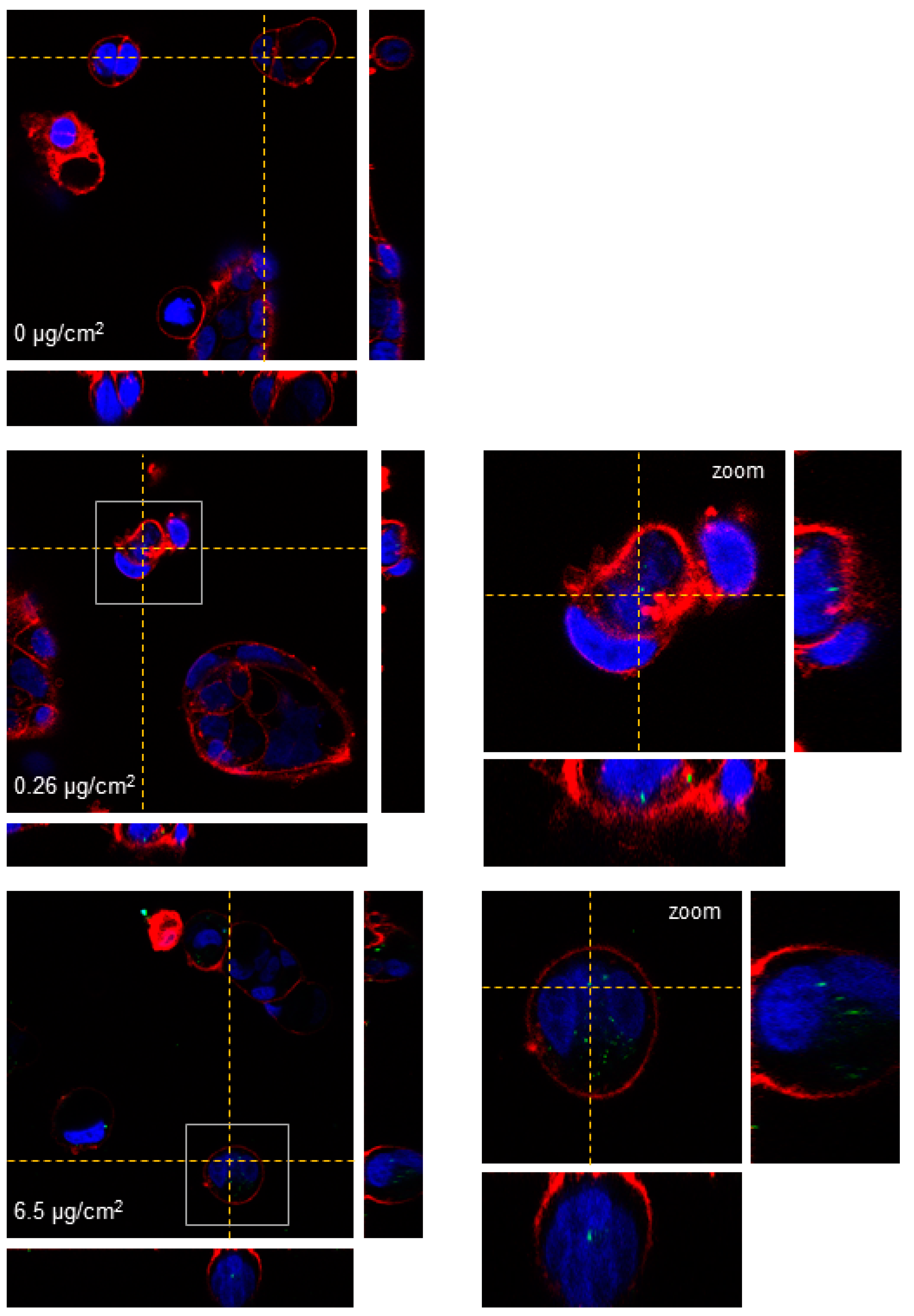

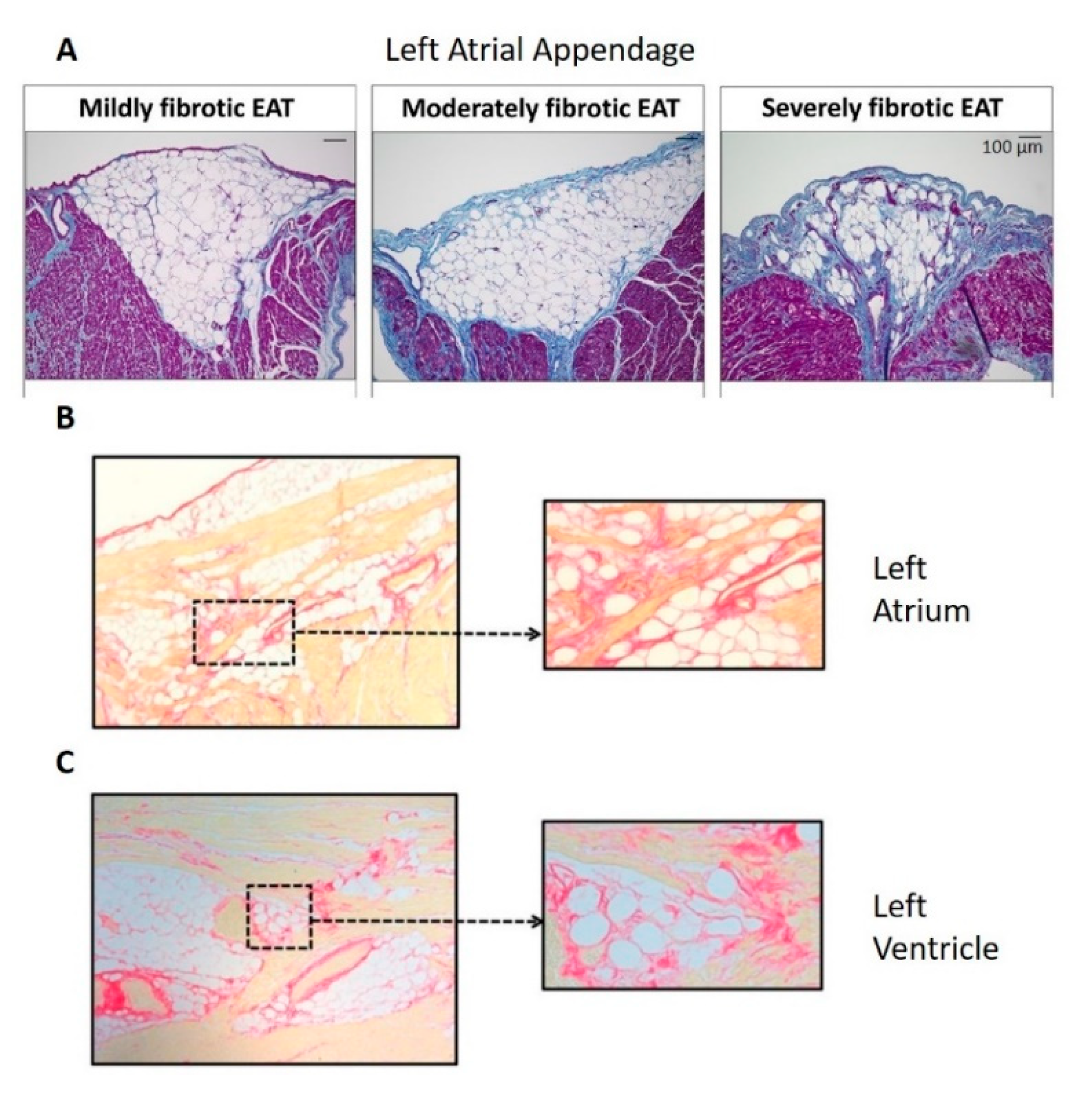

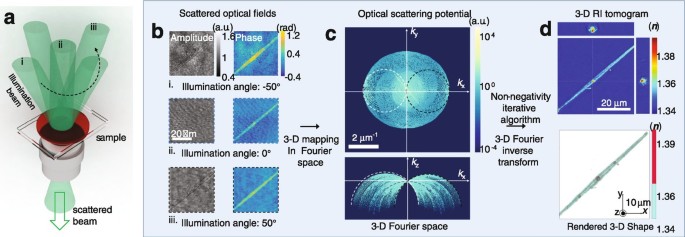













![Expert Answer] Identify the structures in the cell pictured ...](https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/d41/0f74ee3e55de914eb4ce0b4d9f7f3f9e.png)



![Expert Answer] Identify the structures in the cell pictured ...](https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/d97/2b997153979fd7ed20e20b799c515ee4.png)







Post a Comment for "44 identify the structures in the cell pictured on the right. label a label b label c label d label e"